STARTERS
Troubleshooting and Identification/Index
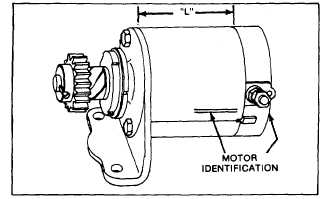
Fig. 46 - Typical 12 VDC Starter Motor
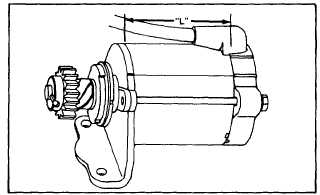
Fig. 47 - Typical 120VAC Starter Motor
TROUBLESHOOTING 12 VOLT & 120 VOLT
STARTING SYSTEMS
The following list is given to aid in diagnosing problems
for 12 volt and 120 volt systems.
NOTE: If a starting problem is encountered, the engine
itself should be thoroughly checked to eliminate it as the
cause of starting difficulty. It is a good practice to check
the engine for freedom of rotation by removing the spark
plug and turning the crankshaft over by hand, to be sure
it rotates freely.
1. Cranks Engine Slowly -
A.
Additional load affecting performance (see note).
B.
Discharged battery (page 11 and 17).
C.
Faulty electrical connection (battery circuit).
D.
Discharged battery (see alternators).
E.
Dirty or worn starter motor commutator, bearing,
weak magnets, etc.
F.
Worn brushes or weak brush spring.
G.
Wrong oil viscosity for temperature expected.
H.
Extension cord longer than 25 feet. (120 volt AC
only)
Motor Identification
Manufacturer Name
(Fig. 46 and 47)
Motor Voltage
Page Number
Briggs & Stratton
3-1/16" L
12
23
Briggs & Stratton
3-3/4" L
12
23
Briggs & Stratton
3-1/2" L
120
23
American Bosch
SMH-12-A11
12
30
American Bosch
SME-12-48
12
30
American Bosch
01965-23-MO-30-SM
12
30
American Bosch
SME-110-C3
120
30
American Bosch
SME-110-C6
120
30
American Bosch
SME-110-C8
120
30
American Bosch
06026-28-M030SM
120
30
Mitsubishi
MMO-5ML
12
30
Mitsubishi
MMO-4FL
12
30
Mitsubishi
M001T02271
12
30
Mitsubishi
V282188
120
30
Motor Products
None
12
10
Fig. 48 - Starter Motor Identification
9