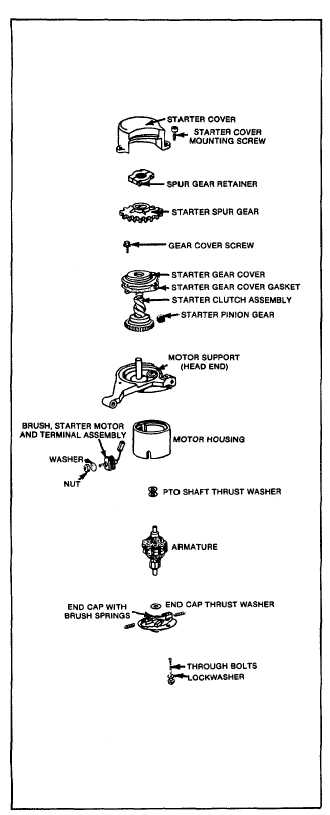
Fig. 50 - Exploded View
The following list is provided to aid in diagnosing
problems.
STARTERS
Nicad System
1.
Cranks Engine Slowly -
A.
Additional starting load affecting performance.
See Note, page 10.
B.
Battery discharged. See Fig. 51.
C.
Faulty battery charger. See Fig. 52.
D.
Poor electrical connection (wiring harness
See Fig. 49.
E.
Starter motor clutch slipping. See page 13.
F.
Brushes sticking in brush holders or worn
brushes. See Fig. 58.
G.
Dirty or worn starter motor commutator. See
page 14 and 15.
H.
Weak magnets.
2.
Engine Will Not Crank -
A.
Discharged or faulty battery. See page 12.
B.
Faulty wiring harness (open circuit). See
Fig. 49.
C.
Faulty starter switch (open circuit). See
Fig. 53.
D.
Open circuit in starter motor itself. See
page 13.
E.
Brushes sticking, etc. See Fig. 58.
3.
Starter Motor Spins;
But Does Not Crank Engine -
A.
Sticking nylon spur gear, due to dirt. See
page 13.
B.
Damaged pinion or starter clutch gear.
See page 13.
C.
Starter motor clutch slipping. See page 13.
D.
Incorrect rotation due to reversed motor
polarity - all motors rotate counterclock-
wise at the pinion gear.
TESTING THE NICKEL CADMIUM
BATTERY AND CHARGER
The following paragraphs describe an inexpensive
battery load tester and a battery charger tester which
may be easily constructed.
BATTERY TESTER
Parts Needed
1.
Two GE sealed beam headlight bulbs #4001.
2.
Briggs & Stratton VOA meter: page 8 or use a
0 to 15 volt DC voltmeter.
3.
Two #70 Miller alligator clips. with #62 insulators.
or a battery connector plug from a wiring harness.
Solder the two headlights together with wires, and
connect the voltmeter as shown in the accompanying
illustration. Fig. 51.
11